• NVMe Over Fabric, • QLC Flash, • 3D XPoint.
Details
Disaggregated, Shared-Everything Storage
VAST’s DASE storage architecture breaks from the idea that scalable storage needs to be built from shared-nothing clusters. When servers are disaggregated from storage, everything is better:
Database Consistency
With VAST’s transactional file system, data is managed using append-on-write semantics. Data is never overwritten in place – new writes are committed to new write stripes via a layer of indirection created through pointers stored in nonvolatile, storage class memory. No volatile caches. No batteries.
Since every write is atomic, the file system can never be corrupted through loss of power or a system crash. Without journals, there is no need for legacy fsck tools.
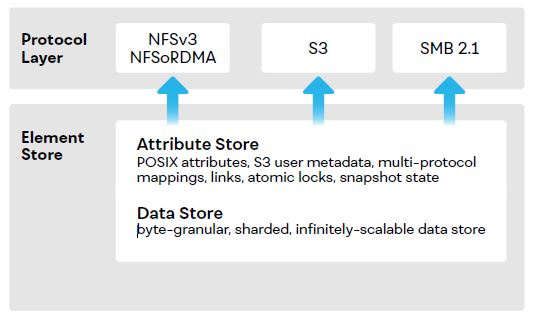
Multi-Protocol System
Each VAST protocol server has direct access to an exabyte-scale global namespace. Data access is fast from any protocol, data is unbounded.
VAST Global QLC Flash Translation
Legacy storage systems were not designed to work with large, multi-GB flash erase blocks and low-endurance drives. While QLC devices cost significantly less than traditional enterprise flash, it takes a new architecture concept to be able to use these devices and ensure over a decade of device longevity.
QLC flash wear leveling is done at the global level, and the system balances the needs of transactional workloads with the needs of archive data to deliver an averaged endurance that is greater than what QLC devices provide themselves.
The DASE cluster architecture leverages TBs to PBs of Storage Class Memory (3D XPoint) to buffer writes into global and persistent fabric-attached memory. VAST’s log-based file system creates a layer of indirection for new writes and appends. This indirection enables the system to only write in full, multi-GB QLC flash erase blocks - vastly reducing garbage collection, and enabling an unnaturally higher level of device endurance.
Moreover, VAST exploits additional context provided by the applications to predictively place data in QLC erase blocks that have a common life expectancy. By eliminating write amplification, VAST systems can be deployed for over a decade… all backed by by VAST Data’s 10-Year Endurance Warrantee.
Global Erasure Codes
VAST has broken the cost vs. reliability trade-off in data protection by developing a new, global approach that provides ground breaking efficiency and resilience.
Shared-nothing storage nodes have CPUs responsible for a limited number of storage devices in a shared-nothing cluster. The VAST DASE architecture, on the other hand, enables any CPU to directly write to 10s to 1,000s of drives simultaneously, making it possible for the system to create very wide write stripes without imposing any cluster cross—talk or erasure code coordination.
Before VAST, the only way to achieve the right balance of performance and write stripe efficiency would be to use large amounts of DRAM, which is both costly and complicates system architectures because of cache power management and coherency issues. The VAST architecture employs 3D XPoint in a fabric-attached, persistent write buffer to enable fast cluster write speeds while also giving the cluster the time to craft large, QLC-optimized write stripes without the need for expensive DRAM and without the need for cache-coherence or batteries.
At the core of nearly every scale-out storage system in the market today is an adaptation of a Reed-Solomon error correction. The basic data reconstruction principle of Reed-Solomon is simple: when a drive within a write stripe is lost, all of the other drives in the system must be read from in order to perform a recovery. When stripes grow very large, Reed Solomon makes large striping impossible because the added time to perform a device rebuild by reading very wide stripes results in an unacceptably high Mean Time to Data Loss (MTTDL).
VAST’s new Global Erasure Codes enable each data protection slice in a write stripe to act as a force-multiplier for cluster rebuild speed. VAST’s de-clustered error correction can recover a failed device in a fraction of the time that it takes Reed-Solomon. As clusters grow, stripes are distributed across enclosures - the overhead of the system goes down to 3% while the system becomes more resilient. VAST’s erasure codes are also fail-in-place, to enable instant recovery.
VAST Data Similarity-Based Data Reduction
VAST has broken the trade-off between data reduction efficiency and performance with its Similarity-Based Data Reduction technology. This breakthrough approach combines the global nature of deduplication with the fine-grained byte-granularity of pattern matching to achieve unprecedented levels of storage efficiency without compromising performance or endurance.
Data is first persisted to 3D XPoint so that write speeds are fast, while the system also has time to do aggressive data reduction in the background, all without wearing down flash.
Data is then chunked and fingerprinted with a variable length hashing algorithm. Unlike conventional deduplication systems, VAST’s hash is not intended to find exact block matches, rather it’s engineered to create a signature of the data used determine the relative distance between other data that is already in the system.
The system then measures the ‘distance’ of new data with other data in the system to find relative similarity, the data is compressed against a cluster of similar blocks, providing the opportunity to find and compress patterns across files with byte-range granularity (1000s of times less sensitive to noise in data than classic deduplication methods).
Data in a similarity cluster is locally decodable, such that the system can simply retrieve the reference block and the deltas to perform a decompressed read within less than a millisecond. You don’t need to decompress petabytes to perform a 4K read, as would be needed with legacy approaches to compressing multiple files.
VAST clusters are in production in some of the most data-intensive environments today. The goal of these deployments is to eliminate reliance on mechanical media and enable consolidation across workflows. The result is faster pipelines and workflows for business-critical applications.
| Manufacturer | Vast |
|---|---|
| Part No. | VAST-DF-5615 |
| End of Life? | No |
| Width | 44.704 |
| Height | 8.6868 |
| Depth | 94.996 |
| Weight [Kg] | 38.55 |
| Rack Units | 2U |
| Compatible CPU(s) | x86 Processors |
| Max CPU Clk Spd | 2.4 GHz |
| Max # Core(s) | 80 |
| Memory Slot(s) | 32 |
| Memory Capacity | 32GB 2400 MHz RDIMM |
| Max. No. of Drive Enclosure(s) | Up to 1,000 |
| Power Consumption | 4 x 1500W |
| LAN Socket(s) | Ethernet (TCP and RDMA) Infiniband |
| Storage Controller | BLOCK (NVMe-oF) and FILE (NFS) Protocols |
| RAID Options | RAID-6, Snapshots Thin Provisioning |



